R&D Blog
Zero Lag Moving Average Filter | Trading Strategy (Entry & Exit)
I. Trading Strategy
Developer: John Ehlers and Ric Way. Source: Ehlers, J., Way, R. (2010). Zero Lag (well, almost). Concept: Trend following trading strategy based on moving average filters. Research Goal: To verify performance of the Zero Lag Moving Average (ZLMA). Specification: Table 1. Results: Figure 1-2. Trade Filter: Long Trades: Zero Lag Moving Average (ZLMA) crosses over Exponential Moving Average (EMA). Short Trades: Zero Lag Moving Average (ZLMA) crosses under Exponential Moving Average (EMA). Portfolio: 42 futures markets from four major market sectors (commodities, currencies, interest rates, and equity indexes). Data: 36 years since 1980. Testing Platform: MATLAB®.
II. Sensitivity Test
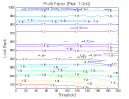
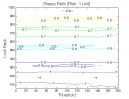
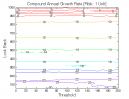
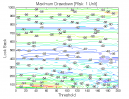
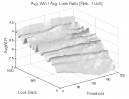
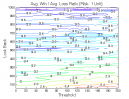
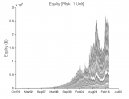
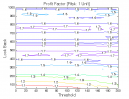
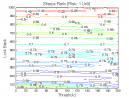
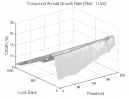
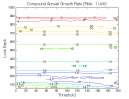
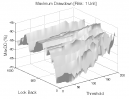
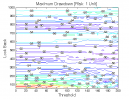
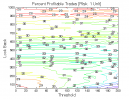
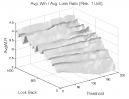
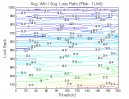
All 3-D charts are followed by 2-D contour charts for Profit Factor, Sharpe Ratio, Ulcer Performance Index, CAGR, Maximum Drawdown, Percent Profitable Trades, and Avg. Win / Avg. Loss Ratio. The final picture shows sensitivity of Equity Curve.
Tested Variables: Look_Back, Threshold (Definitions: Table 1):
Figure 1 | Portfolio Performance (Inputs: Table 1; Commission & Slippage: $0).
| STRATEGY | SPECIFICATION | PARAMETERS |
| Auxiliary Variables: | Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Alpha = 2 / (Look_Back + 1); EMA[i] = Alpha × Close[i] + (1 − Alpha) × EMA[i − 1]; Index: i ~ Current Bar. Zero Lag Moving Average (ZLMA): Alpha = 2 / (Look_Back + 1); ZLMA[i] = Alpha × (EMA[i] + Gain × (Close[i] − ZLMA[i − 1])) + (1 − Alpha) × ZLMA[i − 1]; Index: i ~ Current Bar. Variable Gain (from the ZLMA formula): If the variable Gain is zero, the ZLMA becomes just an EMA. If the Gain is sufficiently large, the ZLMA tracks the price for all practical purposes (i.e. minimum lag and minimum smoothing). Therefore, we seek a value of Gain that is a satisfactory compromise. To get the least amount of error (Error = Close[i] − ZLMA[i]), a loop searches for the best value of Gain by varying the Gain variable from the lower Gain_Limit to the upper Gain_Limit. The default value for the variable Gain_Limit is 5 (this value is further researched in the next blog entry). | Look_Back = [60, 1000], Step = 20; Gain_Limit = 5; |
| Setup: | N/A. | |
| Filter: | Long Signal: ZLMA[i] crosses over EMA[i], and 100*Least_Error / ATR[i] > Threshold Index: i ~ Current Bar. Short Signal: ZLMA[i] crosses under EMA[i], and 100*Least_Error / ATR[i] > Threshold Index: i ~ Current Bar. Note: Error = Close[i] − ZLMA[i]. The Least_Error is an error for the best value of Gain found via a loop which runs bar-by-bar from the lower Gain_Limit to the upper Gain_Limit. In the original paper, the Least_Error is not normalized by the ATR (Average True Range) but by a closing price. This is not adequate for tests on continuous futures contracts and therefore the original formula was adjusted. Mode: The 2-phase reversal system (long/short). | Threshold = [0, 200], Step = 5; |
| Entry: | Long Trades: A buy at the open is placed after a Long Signal. Short Trades: A sell at the open is placed after a Short Signal. | |
| Exit: | Stop Loss Exit: ATR(ATR_Length) is the Average True Range over a period of ATR_Length. ATR_Stop is a multiple of ATR(ATR_Length). Long Trades: A sell stop is placed at [Entry − ATR(ATR_Length) * ATR_Stop]. Short Trades: A buy stop is placed at [Entry + ATR(ATR_Length) * ATR_Stop]. | ATR_Length = 20; ATR_Stop = 6; |
| Sensitivity Test: | Look_Back = [60, 1000], Step = 20 Threshold = [0, 200], Step = 5 | |
| Position Sizing: | Initial_Capital = $1,000,000 Fixed_Fractional = 1% Portfolio = 42 US Futures ATR_Stop = 6 (ATR ~ Average True Range) ATR_Length = 20 | |
| Data: | 42 futures markets; 36 years (1980/01/01−2016/06/30) |
Table 1 | Specification: Trading Strategy.
III. Sensitivity Test with Commission & Slippage
Tested Variables: Look_Back, Threshold (Definitions: Table 1):
Figure 2 | Portfolio Performance (Inputs: Table 1; Commission & Slippage: $100 Round Turn).
IV. Benchmarking
We benchmark the base case strategy against alternatives:
Case #1: Look_Back = 250; Threshold = 100 (Base Case).
Case #2: Look_Back = 500; Threshold = 100.
Case #3: Look_Back = 750; Threshold = 100.
Case #4: Look_Back = 1000; Threshold = 100.
| Fixed Fractional Sizing | Case #1 | Case #2 | Case #3 | Case #4 |
| Net Profit ($) | 299,855,388 | 68,584,149 | 22,802,153 | 6,734,038 |
| Sharpe Ratio | 0.88 | 0.76 | 0.63 | 0.44 |
| Ulcer Performance Index (UPI) | 0.98 | 0.67 | 0.52 | 0.28 |
| Profit Factor | 1.45 | 1.74 | 1.67 | 1.55 |
| CAGR (%) | 17.20 | 12.89 | 9.76 | 6.38 |
| Max. Drawdown (%) | (53.29) | (48.65) | (51.01) | (55.59) |
| Percent Profitable Trades (%) | 31.13 | 32.82 | 30.68 | 27.98 |
| Avg. Win / Avg. Loss Ratio | 3.20 | 3.56 | 3.77 | 3.99 |
Table 2 | Inputs: Table 1; Fixed Fractional Sizing: 1%; Commission & Slippage: $100 Round Turn.
V. Research
Ehlers, J., Way, R. (2010). Zero Lag (well, almost):
All smoothing filters and moving averages have lag. It’s a law. The lag is necessary because the smoothing is done using past data. Therefore, the averaging includes the effects of the data several bars ago. In this article we show you how to remove a selected amount of lag from an Exponential Moving Average (EMA). Removing all the lag is not necessarily a good thing because with no lag the indicator would just track out the price you are filtering. That is, the amount of lag removed is a tradeoff with the amount of smoothing you are willing to forgo.
VI. Rating: Zero Lag Moving Average Filter | Trading Strategy
A/B/C/D
VII. Summary
The trading strategy based on the Zero Lag Moving Average does not perform significantly better than the strategy based on the Hull Moving Average or some other alternatives.
Related Entries: Zero Lag Moving Average Filter (Entry & Filter) | Simple Moving Average Filter (Entry & Exit) | Hull Moving Average Filter (Entry & Exit)
Related Topics: (Public) Trading Strategies
CFTC RULE 4.41: HYPOTHETICAL OR SIMULATED PERFORMANCE RESULTS HAVE CERTAIN LIMITATIONS. UNLIKE AN ACTUAL PERFORMANCE RECORD, SIMULATED RESULTS DO NOT REPRESENT ACTUAL TRADING. ALSO, SINCE THE TRADES HAVE NOT BEEN EXECUTED, THE RESULTS MAY HAVE UNDER-OR-OVER COMPENSATED FOR THE IMPACT, IF ANY, OF CERTAIN MARKET FACTORS, SUCH AS LACK OF LIQUIDITY. SIMULATED TRADING PROGRAMS IN GENERAL ARE ALSO SUBJECT TO THE FACT THAT THEY ARE DESIGNED WITH THE BENEFIT OF HINDSIGHT. NO REPRESENTATION IS BEING MADE THAT ANY ACCOUNT WILL OR IS LIKELY TO ACHIEVE PROFIT OR LOSSES SIMILAR TO THOSE SHOWN.
RISK DISCLOSURE: U.S. GOVERNMENT REQUIRED DISCLAIMER | CFTC RULE 4.41
Codes: matlab/ehlers/zeroLag